Naturaliste Plateau on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
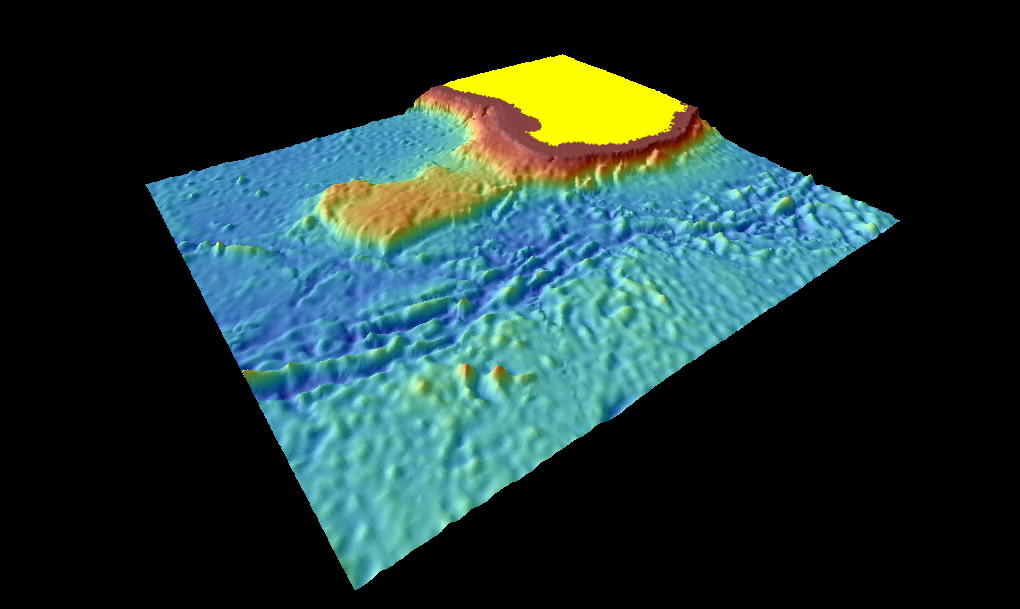 The Naturaliste Plateau is one of several large submarine plateaus extending from
The Naturaliste Plateau is one of several large submarine plateaus extending from
.
 The Naturaliste Plateau is one of several large submarine plateaus extending from
The Naturaliste Plateau is one of several large submarine plateaus extending from Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
into the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
. It is a rectilinear plateau that covers an area of 90,000 square kilometres. Its width is about east-west and north-south. The water depths are from 1500 to 5000 metres.
The Mentelle Basin and Naturaliste Trough
''Naturaliste'' is the fifth studio album by the Australian indie pop trio, the Lucksmiths, which was released on 10 March 2003 via Candle Records (catalogue number LUCKY16). The band members Marty Donald on guitar, backing vocals and glocken ...
lie between the mainland and this plateau. The plateau is bordered by the Perth Abyssal Plain in the north and west and the Australian-Antarctic Basin in the south.Naturaliste Plateau: Regional setting.
Geoscience Australia
Geoscience Australia is an agency of the Australian Government. It carries out geoscientific research. The agency is the government's technical adviser on all aspects of geoscience, and custodian of the geographic and geological data and knowl ...
.
It is located within the Australian marine park known as the South-west Corner Marine Park
The South-west Corner Marine Park (formerly South-west Corner Commonwealth Marine Reserve) is a marine protected area on the lower south west and southern coast of Western Australia, one of 14 in the South-west Marine Parks Network.
It was ga ...
.
The Naturaliste Plateau formed during the Early Cretaceous 136 Ma when Australia and India broke up and during the Late Cretaceous 83 Ma when Australia and Antarctica broke up. Lavas and intrusive rocks on the plateau flanks have ages of between 132-128 Ma. The volcanic sequence that consists of alternating basaltic flows and volcaniclastic beds, cut by multiple dikes, was recovered at IODP Site U1513 on the eastern flank. After the volcanic eruption, the Naturaliste Plateau subsided from shelf to bathyal depths during the Early Cretaceous. The eastern flank of the plateau slopes relatively gently, while the other three flanks are relatively steep. The southern flank formed during the Australia-Antarctica break-up, the other flanks during the rifting between India and Australia. The continent ocean transition (COT) is wide on the north side and on the southern side where the plateau is flanked by the Diamantina Fracture Zone
The Diamantina Fracture Zone (DFZ) is an area of the south-eastern Indian Ocean seafloor, consisting of a range of ridges and trenches. It lies to the south of the mideastern Indian Ocean features of the Wharton Basin and Perth Basin, and ...
.
Before India broke off from Australia-Antarctica at 127 Ma the Naturaliste Plateau was flanked by what would become two microcontinent
Continental crustal fragments, partly synonymous with microcontinents, are pieces of continents that have broken off from main continental masses to form distinct islands that are often several hundred kilometers from their place of origin.
Caus ...
s, the Batavia
Batavia may refer to:
Historical places
* Batavia (region), a land inhabited by the Batavian people during the Roman Empire, today part of the Netherlands
* Batavia, Dutch East Indies, present-day Jakarta, the former capital of the Dutch East In ...
and Gulden Draak Knolls, now located on the western margin of the Perth Abyssal Plain from Australia. South of the plateau, during some 45 Ma after India and the two knolls broke off, rifting occurred between the plateau and the Bruce Rise Bruce Spur (also known as Banka Brus or Bruce Rise) is an undersea spur off Antarctica. The name was approved by the Advisory Committee for Undersea Features in September 1963.
The Bruce Spur is divided into two distinct segments separated by The n ...
, now located off Antarctica. This rifting continued until sea-floor spreading began 83 Ma.
Continental metamorphic
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causin ...
and granitic
A granitoid is a generic term for a diverse category of coarse-grained igneous rocks that consist predominantly of quartz, plagioclase, and alkali feldspar. Granitoids range from plagioclase-rich tonalites to alkali-rich syenites and from quart ...
basement rocks have been dredged from both knolls. Protolith
A protolith () is the original, unmetamorphosed rock from which a given metamorphic rock is formed.
For example, the protolith of a slate is a shale or mudstone. Metamorphic rocks can be derived from any other kind of non-metamorphic rock and thu ...
granite from Gulden Draak was emplaced in either the Australian Yilgarn Craton
The Yilgarn Craton is a large craton that constitutes the bulk of the Western Australian land mass. It is bounded by a mixture of sedimentary basins and Proterozoic fold and thrust belts. Zircon grains in the Jack Hills, Narryer Terrane have b ...
or the Antarctic Mawson Craton
Sir Douglas Mawson OBE FRS FAA (5 May 1882 – 14 October 1958) was an Australian geologist, Antarctic explorer, and academic. Along with Roald Amundsen, Robert Falcon Scott, and Sir Ernest Shackleton, he was a key expedition leader durin ...
2850 Ma. The Mesoproterozoic crust from this knoll is coeval with crust from the Naturaliste Plateau. Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is ...
-Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
(540–530 Ma) granite gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures an ...
es from the Batavia Knoll were emplaced during or after the formation of the Kuunga Orogen
The Kuunga orogeny (from Swahili, "to unite") was an orogeny that occurred in South-east Africa during the Ediacaran and Cambrian. Composed of three separate orogenic belts (Damara, Zambesi, and Lurio) that are slightly younger than the East A ...
.
References
; Notes ; Sources * {{coord, -34.1, 111.3, dim:500000_region:AU, display=title Plateaus of the Indian Ocean Coastline of Western Australia Exclusive economic zone of Australia